[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
Which of the following statements is true:
I. American options can only be exercised at expiry
II. European options can be exercised at any time up to expiry
III. Bermudan options can be exercised at any time up to expiry except at certain times
IV. A European option can never be worth more than an American option
A risk manager is deciding between using futures or forward contracts to hedge a forward foreign exchange position. Which of the following statements would be true as he considers his decision:
I. He would need to consider tailing the hedge for the futures contracts while that does not apply to forward contracts
II. He would need to consider tailing the hedge for the forward contract while that does not apply to futures contracts
III. He would need to consider counterparty risk for the futures contracts while that is unlikely to be an issue for the forward contract
IV. He would be likely able to match up maturity dates to his liability when using futures while that may not be so for the forward contracts
A zero coupon bond matures in 5 years and is yielding 5%. What is its modified duration?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. An interest rate swap is equivalent to the swap counterparties placing deposits with each other, one carrying a fixed rate of interest and the other a floating rate
II. The parties to a currency swap exchange principals
III. The risky leg in an IRS is the floating rate leg
IV. Swaps do not carry counterparty risks
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
A long call position in an asset-or-nothing option has the same payoff as:
A borrower who fears a rise in interest rates and wishes to hedge against that risk should:
The local coefficient of risk aversion for a utility function u(x) where x is wealth is expressed as:
A)

B)

C)
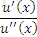
D)
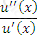
If the 3 month interest rate is 5%, and the 6 month interest rate is 6%, what would be the contract rate applicable to a 3 x 6 FRA?
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
Which of the following best describes a writer extendible option
Arrange the following rates in descending order, assuming an upward sloping yield curve:
1. The 10 year zero rate
2. The forward rate from year 9 to 10
3. The yield-to-maturity on a 10 year coupon bearing bond
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Cash markets tend to be more liquid than derivative markets
II. A higher credit risk is associated with lower liquidity in times of crises
III. A higher bid-ask spread indicates greater liquidity when compared to a lower bid-ask spread
IV. A higher normal market size indicates greater liquidity than a lower market size
When hedging one fixed income security with another, the hedge ratio is determined by:
According to the dividend discount model, if d be the dividend per share in perpetuity of a company and g its expected growth rate, what would the share price of the company be. 'r' is the discount rate.
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Rebalancing frequency is a consideration for a risk manager when assessing the adequacy of delta hedging procedures on an options portfolio
II. Stock options granted to employees that are exercisable 5 years in the future will lead to a decline in the share price 5 years hence only if the options are exercised.
III. In a delta neutral portfolio, theta is often used as a proxy for gamma by traders.
IV. Vega is highest when the option price is close to the strike price
A fund manager buys a gold futures contract at $1000 per troy ounce, each contract being worth 100 ounces of gold. Initial margin is $5,000 per contract, and the exchange requires a maintenance margin to be maintained at $4,000 per contract. Prices fall the next day to $980. What is the margin call the fund manager faces in respect of daily variation margin ?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. The Kappa family of indices take only downside risk into account
II. The Treynor ratio provides information on the excess return per unit of specific risk
III. All else remaining constant, the Sharpe ratio for a portfolio will increase as we increase leverage by borrowing and investing in the risky bundle
IV. In the market portfolio, we can expect Jensen's alpha to equal zero.
A refiner may use which of the following instruments to simultaneously protect against a fall in the prices of its products and a rise in the prices of its inputs:
It is January and an Australian importer needs to pay USD 1,120,000 at the end of August to a US creditor. If a AUD/USD futures contract is trading on the exchange at a futures price of 0.6750 (ie, 1 AUD = 0.6750 USD), and the contract size is USD 100,000, what would represent an appropriate hedge?
In terms of notional values traded, which of the following represents the largest share of total traded futures and options globally?
It is October. A grower of crops is concerned that January temperatures might be too low and destroy his crop. A heating-degree-days futures contract (HDD futures contract) is available for his city. What would be the best course of action for the grower?
A and B are two stocks with normally distributed returns. The returns for stock A have a mean of 5% and a standard deviation of 20%. Stock B has a mean of 3% and standard deviation of 5%. Their correlation is -0.6. What is the mean and volatility of a portfolio which holds stocks A and B in the ratio 6:4?
If the 1-year forward rates for years 1,2,3 and 4 are 2%, 3%, 4% and 5% respectively, what is the zero coupon spot rate for 4 years
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Implied volatility refers to volatility estimates made by risk managers for their VaR calculations
II. Implied volatility is generally observed to be constant across strikes and expiries, as otherwise we would have riskless arbitrage possible.
III. Volatility smile refers to the shape of the implied volatility curve across different strike prices
IV. An option portfolio cannot have negative theta
Which of the following is NOT a historical event which serves as an example of a short squeeze that happened in the markets?
Which of the following are valid reasons that explain an upward sloping yield curve?
I. The market expects interest rates to increase in the future
II. The market expects interest rates to decline in the future
III. Investors prize liquidity over illiquidity
IV. Investors believe the economy is likely to enter recession
An investor can use which of the following to replicate a fixed for floating interest rate swap where the investor pays fixed and receives floating?
I. Long positions in a series of forward rate agreements (FRAs)
II. A short position in a fixed rate bond and a long position in a floating rate note
III. A long position in a floating rate note and a short position in an FRA
IV. A long position in an interest rate cap and a short position in an interest rate floor at the same strike
Which of the following statements is true:
I. On-the-run bonds are priced higher than off-the-run bonds from the same issuer even if they have the same duration.
II. The difference in pricing of on-the-run and off-the-run bonds reflects the differences in their liquidity
III. Strips carry a coupon generally equal to that of similar on-the-run bonds
IV. A low bid-ask spread indicates lower liquidity
Which of the following is not a relevant consideration for a trader desirous of delta hedging his or her options portfolio?
Which of the following will have a higher reinvestment risk when compared to a 6% bond issued at par? Assume all bonds have identical yield to maturity.
I. A coupon bearing bond with a coupon rate of 2%
II. An amortizing bond
III. A coupon bearing bond with a coupon rate of 11%
IV. A zero coupon bond
A treasury bond paying a 4% coupon is sold at a discount. Assume that the yield curve stays flat and constant over the next one year. The price of the bond one year hence can be expected to:
Credit derivatives can be used for:
I. Reducing credit exposures
II. Reducing interest rate risks
III. Earn credit risk premiums
IV. Get market exposure without taking cash market positions


