Which of the following are valid techniques used when performing stress testing based on hypothetical test scenarios:
I. Modifying the covariance matrix by changing asset correlations
II. Specifying hypothetical shocks
III. Sensitivity analysis based on changes in selected risk factors
IV. Evaluating systemic liquidity risks
The probability of default of a security over a 1 year period is 3%. What is the probability that it would have defaulted within 6 months?
Which of the following are true:
I. Monte Carlo estimates of VaR can be expected to be identical or very close to those obtained using analytical methods if both are based on the same parameters.
II. Non-normality of returns does not pose a problem if we use Monte Carlo simulations based upon parameters and a distribution assumed to be normal.
III. Historical VaR estimates do not require any distribution assumptions.
IV. Historical simulations by definition limit VaR estimation only to the range of possibilities that have already occurred.
A Monte Carlo simulation based VaR can be effectively used in which of the following cases:
There are two bonds in a portfolio, each with a market value of $50m. The probability of default of the two bonds are 0.03 and 0.08 respectively, over a one year horizon. If the probability of the two bonds defaulting simultaneously is 1.4%, what is the default correlation between the two?
A zero coupon corporate bond maturing in an year has a probability of default of 5% and yields 12%. The recovery rate is zero. What is the risk free rate?
For an equity portfolio valued at V whose beta is β, the value at risk at a 99% level of confidence is represented by which of the following expressions? Assume σ represents the market volatility.
A risk analyst attempting to model the tail of a loss distribution using EVT divides the available dataset into blocks of data, and picks the maximum of each block as a data point to consider.
Which approach is the risk analyst using?
Assuming all other factors remain the same, an increase in the volatility of the returns on the assets of a firm causes which of the following outcomes?
The principle underlying the contingent claims approach to measuring credit risk equates the cost of eliminating credit risk for a firm to be equal to:
What would be the correct order of steps to addressing data quality problems in an organization?
Which of the following statements is true in respect of a non financial manufacturing firm?
I. Market risk is not relevant to the manufacturing firm as it does not take proprietary positions
II. The firm faces market risks as an externality which it must bear and has no control over
III. Market risks can make a comparative assessment of profitability over time difficult
IV. Market risks for a manufacturing firm are not directionally biased and do not increase the overall risk of the firm as they net to zero over a long term time horizon
Which of the following is not a risk faced by a bank from holding a portfolio of residential mortgages?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Shocks to risk factors should be relative rather than absolute if we wish to avoid a change in the sign of the risk factor.
II. Interest rate shocks are generally modeled as absolute shocks.
III. Shocks to volatility are generally modeled as absolute shocks.
IV. Shocks to market spreads are generally modeled as relative shocks.
Which of the following is true in relation to Principal Component Analysis (PCA)?
I. An n x n positive definite square matrix will have n-1 eigenvectors
II. The eigenvalues for a correlation matrix can be derived from the corresponding values for the covariance matrix
III. Principal components are uncorrelated to each other
IV. PCA is useful as it allows 100% of the variation in a complex system to be explained by the first three principal components
Company A issues bonds with a face value of $100m, sold at issuance at $98. Bank B holds $10m in face of these bonds acquired at a price of $70. What is Bank B's exposure to the debt issued by Company A?
Loss from a lawsuit from an employee due to physical harm caused while at work is categorized per Basel II as:
If the default hazard rate for a company is 10%, and the spread on its bonds over the risk free rate is 800 bps, what is the expected recovery rate?
For the purposes of calculating VaR, an FRA can be modeled as a combination of:
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Liquidity risks during time of crisis may be exacerbated by large collateral calls continuing over a period of time.
II. Stress tests are always separately modeled from VaR computations which cannot deal with stress scenarios of the kind considered in stress tests.
III. A maximum loss scenario considers the maximum possible loss given a 'plausibility constraint' that is based upon the joint probability of such a loss happening
According to the implied capital model, operational risk capital is estimated as:
Which of the following statements is true?
I. Real Time Gross Systems (RTGS) for large value payments consume less system liquidity than Deferred Net Systems (DNS)
II. The US Fedwire is an example of a Real Time Gross System
III. Current disclosure requirements in relation to liquidity risk as laid down in the Basel framework require banks to disclose how liquidity stress scenarios were formulated
IV. A CFP (Contingency Funding Plan) provides access to Central Bank financing
Which of the following credit risk models focuses on default alone and ignores credit migration when assessing credit risk?
Which of the following describes rating transition matrices published by credit rating firms:
Which of the following is not a tool available to financial institutions for managing credit risk:
CreditRisk+, the actuarial model for calculating portfolio credit risk, is based upon:
Which of the following is true in relation to a Contingency Funding Plan (CFP)?
I. A CFP is like a disaster recovery plan to deal with a liquidity crisis
II. A CFP should consider market stress conditions, but failures of payment systems are not relevant as they fall under the remit of operational risk
III. Reputational damage may result if the market finds out that a firm has had to execute its CFP
IV. Sources of emergency funding considered in the CFP should include the role of the central bank as the lender of last resort
For a 10 year interest rate swap, what would be the worst time for a counterparty to default (in terms of the maximum likely credit exposure)
If the full notional value of a debt portfolio is $100m, its expected value in a year is $85m, and the worst value of the portfolio in one year's time at 99% confidence level is $60m, then what is the credit VaR?
Which of the following is not a permitted approach under Basel II for calculating operational risk capital
Which of the following is not a limitation of the univariate Gaussian model to capture the codependence structure between risk factros used for VaR calculations?
The cumulative probability of default for a security for 4 years is 11.47%. The marginal probability of default for the security for year 5 is 5% during year 5. What is the cumulative probability of default for the security for 5 years?
Calculate the 1-year 99% credit VaR of a portfolio of two bonds, each with a value of $1m, and the probability of default of 1% each over the next year. Assume the recovery rate to be zero, and the defaults of the two bonds to be uncorrelated to each other.
If F be the face value of a firm's debt, V the value of its assets and E the market value of equity, then according to the option pricing approach a default on debt occurs when:
For a FX forward contract, what would be the worst time for a counterparty to default (in terms of the maximum likely credit exposure)
As part of designing a reverse stress test, at what point should a bank's business plan be considered unviable (ie the point where it can be considered to have failed)?
Between two options positions with the same delta and based upon the same underlying, which would have a smaller VaR?
For credit risk calculations, correlation between the asset values of two issuers is often proxied with:
Identify the correct sequence of events as it unfolded in the credit crisis beginning 2007:
I. Mortgage defaults increased
II. Collapse in prices of unrelated assets as banks tried to create liquidity
III. Banks refused to lend or transact with each other
IV. Asset prices for CDOs collapsed
For identical mean and variance, which of the following distribution assumptions will provide a higher estimate of VaR at a high level of confidence?
Under the CreditPortfolio View model of credit risk, the conditional probability of default will be:
Monte Carlo simulation based VaR is suitable in which of the following scenarios:
I. When no assumption can be made about the distribution of underlying risk factors
II. When underlying risk factors are discontinuous, show heavy tails or are otherwise difficult to model
III. When the portfolio consists of a heterogeneous mix of disparate financial instruments with complex correlations and non-linear payoffs
IV. A picture of the complete distribution is desired in addition to the VaR estimate
When fitting a distribution in excess of a threshold as part of the body-tail distribution method described by the equation below, how is the parameter 'p' calculated.
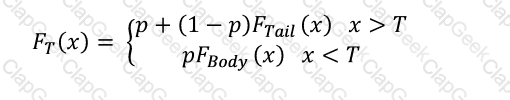
Here, F(x) is the severity distribution. F(Tail) and F(Body) are the parametric distributions selected for the tail and the body, and T is the threshold in excess of which the tail is considered to begin.
Under the KMV Moody's approach to calculating expecting default frequencies (EDF), firms' default on obligations is likely when:
Under the standardized approach to calculating operational risk capital under Basel II, negative regulatory capital charges for any of the business units:
For a hypotherical UoM, the number of losses in two non-overlapping datasets is 24 and 32 respectively. The Pareto tail parameters for the two datasets calculated using the maximum likelihood estimation method are 2 and 3. What is an estimate of the tail parameter of the combined dataset?
Which of the following are considered counterparty based credit enhancements?
I. Collateral
II. Credit default swaps
III. Close out netting arrangements
IV. Guarantees


