Synovial fluid is actually quite viscous and does not have the same consistency as plasma. The reason for its thicker consistency is to provide cushion and reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement.
Urinalysis & Other Body Fluids
All of the statements below about synovial fluid are true EXCEPT:
Mode is defined as the number that occurs most frequently in a set of numbers.
The value that occurs most frequently in a set of results or values would be termed:
Either immunofixation or immunoelectrophoresis can be used to confirm Bence-Jones proteinuria.
Which of the following methods would be used to confirm the presence of Bence-Jones protein in the urine:
Valine substitutes for glutamic acid in the Beta 6 position to produce HbS.
To produce hemoglobin S, glutamic acid that is normally present in the sixth position on the beta globin chain is substituted with which of the following?
What component is indicated for patients who receive directed donations from immediate family members to prevent transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD)?
Which one of the following conditions is NOT associated with hereditary spherocytosis?
The body compensates for alkalosis or acidosis of the blood PRIMARILY to regain a normal pH, between 7.35 - 7.45.
When the body compensates for a respiratory or metabolic disorder, the MAIN goal is to achieve:
Immunoassay is the most common technique that is used by clinical laboratories for therapeutic drug monitoring.
Most of the drugs commonly assessed with TDM can be measured on analytical platforms which utilize antibodies (in some form) for detection. Antibodies can be developed that recognize drugs. Although most drugs are much too small to evoke an immune response, scientists can conjugate drugs to immunogenic proteins to produce antibodies that recognize drug-specific epitopes.
Which of the following is the most common technique that is used by clinical laboratories for therapeutic drug monitoring?
Serum alkaline phosphatase is produced in the bone, intestine, and the placenta- but not in the brain.
Serum alkaline phosphatase activity is derived from all of the following organs except:
A laboratory scientist is working the night shift at a local hospital when the power goes out. What is the course of action to continue to provide laboratory results?
Most anticoagulants in blood collectiong tubes prevent clotting by:
Question options:
Basophilic stippling is the term used to describe red blood cells that contain tiny particles of RNA within their cytoplasm. Basophilic stippling is associated with many conditions, but is strongly associated with lead poisoning.
Multiple small, dark blue particles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of erythrocytes is/are called:
Conversion of only the slant to a pink color in a Christensen's urea agar slant is produced by bacterial species that have weak urease activity. The reaction in the slant to the right is often produced by Klebsiella species, as an example. Strong urease activity is indicated by conversion of the slant and the butt of the tube to a pink color, as seen in the tube to the left. The slant only reaction in the right tube may be seen early on if only the slant had been inoculated; however, with a strong urease producer, both the slant and the butt would turn. Therefore, the reaction is dependent on the strength of urease activity. If the media had outdated for a prolonged period, either there would be no reaction or the appearance of only a faint pink tinge, either in the slant, the butt or both, again depending on the strength of urease production by the unknown organism.
The urease reaction seen in the Christensen's urea agar slant on the far right indicates:

The term that is used to describe the color in these tubes of CSF is "xanthochromia." Xanthochromia is an abnormal color, usually yellow, orange, or pink, in the supernatant of the CSF sample. It may indicate that a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has occurred.

Jaundice and icterus both describe a yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and eyes. Blood plasma/serum that is deep yellow is also described as icteric.
What term is used to describe the color in these tubes of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
In excess triglycerides, the triglycerides reduce the amount of cholesterol in LDL particles producing small dense LDL molecules. Because of size and density, these molecules more easily enter damaged endothelium and vessel walls and are more easily incorporated as plaque is formed.
Which statement best describes small dense LDL particles that can occur in atherogenic dyslipidemia?
Although cysteine-blood agar was traditionally used, F. tularensis will also grow on commercially available Thayer-Martin and chocolate agar which have been enriched with supplemental nutrients.
Which of the following media would you use to isolate Francisella tularensis:
All of the following have been an inspection deficiency for CLIA-approved laboratories except:
AHG must be added to the cells immediately following washing. Antibodies may elute from the cells if the cells are allowed to sit in saline without the addition of AHG.
Which one of the following may cause a FALSE-NEGATIVE result with antiglobulin techniques?
Kell, Kidd, and Duffy are usually warm reacting IgG antibodies. The most common P system antibody is anti-P1, which is a frequently naturally occurring low titer IgM antibody, seen in most P2 individuals.
Blood bank
Which of the following blood groups is most frequently associated with cold agglutinins:
The lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio is a test for assessing fetal lung maturity that is useful in determining risk of an infant born with respiratory distress syndrome.
The Lecithin/Sphingomyelin ratio determination of amniotic fluid is useful in assessing the probability of:
The document designed to protect phlebotomists from contacting hepatitis is the:
In order to perform a venipuncture on a newly admitted hospital patient, a phlebotomist needs to
The type of isolation category that always requires a HEPA mask or respirator to be worn is:
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a structured study that determines the underlying causes of adverse events. RCA focuses on systems, processes, and common causes that were involved in the adverse event. It then determines ways to prevent recurrence by identifying potential improvements in systems and processes that should decrease the likelihood of repeating the event.
Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) is used to evaluate a process prior to its implementation. Its purpose is to identify ways in which a process might possibly fail with the goal being to eliminate or reduce the likelihood of such a failure.
Monitoring quality indicators is important in the maintenance of quality health care. Quality indicators should be identified to prevent medical errors from occurring or to prevent the recurrence of a quality issue. However, it is not the method that is used to evaluate an adverse event after it has occurred.
A medical record audit may be a part of a root cause analysis.
A medical event occurs that results in serious injury to a patient. All systems, processes, and common causes that were involved in the adverse event should be evaluated. A method that can be implemented to effectively study the underlying causes is known as:
Which EBV markers would be MOST likely positive for an individual who had infectious mononucleosis 9 years ago?
What amount of absorbent material must be included between the primary receptacle and secondary packaging for either a category A or category B liquid specimen?
Antibodies in the Rh system typically exhibit which one of the following characteristics?
The production of long, tapered phialides is one of the key identifying features of Trichoderma species. In contrast, Penicillium species, produce phialides with blunt ends.

The phialides of Beauveria species are geniculate, forming a zig-zag pattern.
The arrows in the image on the right point to single, long, tapered phialides that extend laterally from either side of the hyphae. This is an identifying feature of which of the fungi listed below?
Pluripotential stem cells are ultimately capable of differentiating into all types of leukocytes.
Hematology
Pluripotential stem cells are capable of producing which of the following:
Eosinophils do not have cytoplasm containing large purple/blue-staining granules. Instead, their granules are large but are orange/red in color. These granules are very distinctive for this type of cell, typically making their identification simple.
ll of the following statements describe an eosinophil EXCEPT:
High triglycerides may be caused by disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypothyroidism, Cushing's sydnrome, liver disease, uremia, dysglobulinemia, nephrotic syndrome, and alcoholism can cause hypertriglyceridemia.
A 46-year old known alcoholic with liver damage is brought in the ER unconscious. One would expect his lipid values to be affected in what way?
Serum ferritin is a good indicator of iron deficiency. However, it acts like an acute phase reactant, being elevated in a large number of conditions. Patients who have iron deficiency as well as another condition that elevates serum ferritin levels may therefore have normal or even elevated serum ferritin levels.
Which one of the following statements about serum ferritin are true:
Bacterial contamination can manifest itself in several ways including: the presence of clots, darker purple-black color of blood unit, unit can appear cloudy, hemolysis may be present.
During routine inspection, a unit of unexpired blood was noticed to have a black color with numerous small clots. What is the likely cause for this observation?
The personal protective equipment (PPE) that is used in the laboratory to protect the personnel when performing tests on patient blood samples is which of the following:
A combination of (nonselective) 5% sheep blood and (selective) MacConkey agars is sufficient for the recovery of the pathogenic microorganisms that are most commonly encountered in urinary tract infections (UTIs). MacConkey is the selective culture medium that is most commonly used to inhibit growth of gram-positive organisms (most UTIs are caused by gram-negative organisms).
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) is a selective agar that also inhibits the growth of gram-positive organisms. Therefore, using only a combination of MacConkey and EMB would prevent the detection of a gram-positive organism, if this were the cause of the infection.
Chocolate agar or other enriched media may be needed in addition to blood and MacConkey if a more fastidious organism is suspected.
Thayer-Martin would be used specifically for recovery of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Thayer-Martin (or Modified Thayer-Martin) inhibits other microorganisms and allows the selective recovery of both N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis.
Microbiology
Which culture agar combinations below will usually be sufficient for MOST routine urine culture investigations?
The Bethesda assay is used to measure the titer and activity of the antibody present in a patient's sample. Prothrombin time is an initial screening procedure for bleeding disorders and a test used for monitoring anticoagulant therapy. A thrombin time is used to detect heparin interference in an aPTT mixing study. A mixing study is performed to detect the presence of a factor deficiency or coagulation inhibitor, but does not quantify the result.
Hematology
Which of the following tests is used to quantify a coagulation inhibitor?
Medical Technology is the profession concerned with performing laboratory analyses
Leptin signals the hypothalamus that there are changes in fat stores.
Resistin increases insulin resistance and enhances adhesion molecules present on endothelial cells.
IL-6 responds to tissue injury. IL-6 increases insulin resistance by inhibiting insulin receptor signal transduction in liver cells. It also increases other inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1 (IL-1) and TNF-a, and stimulates the liver to produce C-reactive protein (CRP).
Adipose tissue and liver cells produce angiotensinogen, a precursor of angiotensin II. Besides increasing blood pressure, angiotensin II may stimulate adipose cell formation and thus increase adipose mass.
Which one of the following adipocyte products is an important messenger in metabolism, signaling the hypothalamus that there are changes in fat stores?
Haemophilus influenzae is both X and V factor dependent for growth, and is the most common cause of obstructive laryngitis and epiglottitis. H. parainfluenzae is only V-factor dependent and causes only mild pharyngitis, rarely obstructive in nature. H. aphrophilus can be part of the normal upper respiratory flora in humans, does not cause pharyngitis, and is not X or V-factor dependent for growth. Although H. haemolyticus is both X and V-factor dependent, it is beta hemolytic on blood agar and is generally considered non pathogenic.
Acute obstructive epiglottitis, both in adults and children, is caused by the bacterial species shown in this split screen photograph. The colonies recovered on chocolate agar (upper frame) required both hematin and NAD, (as shown by colony growth only between the X and V strips in the lower frame). The most likely identification is:

Which area of the laboratory is responsible for blood coagulation studies that test for the patient's ability to clot their blood?
Which of the following legislation was developed to protect the privacy of all patient information in the health care?
Flow cytometry employs a combination of fluorescent antibody tagging of cells and analysis with laser light scatter.
What principle(s) of flow cytometry are employed when performing immunophenotyping:
The laboratory employee with an 2-year associate degree who performs clinical testing is the:
Estriol levels in conjunction with hCG and AFP can be obtained during pregnancy to:
Sally is seeing her new primary care provider for the first time. When she signs in, she is asked to sign papers for the release of medical records, including her laboratory results. According to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), she must authorize release of records before _______________would be permitted to receive and review her records.
Skeletal deformations result from the increased erythropoiesis that occurs in beta thalassemia major. Children with beta thalassemia intermedia may demonstrate some facial bone deformity, however this is not common. Beta thalassemia minor rarely causes any physical signs or symptoms and beta thalassemia minima is completely asymptomatic.
Skeletal deformations are most commonly present in which of the following beta thalassemias?
n reporting out Gram stains, one should not go beyond what objective observation will allow. In this case, bacterial cells are observed, which are spherical and gram-positive. Their arrangement in tetrads and clusters might be helpful to the physician, suggesting staphylococci. However, one should stop short of naming staphylococci in an official report, as the large gram-positive cocci in tetrads is also suggestive of Micrococcus species, for which human infections have not been reported.
A Gram stain of the serous exudate is shown in the image. The appropriate report would read:
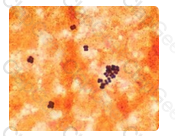
The microscopic features shown here represent Scopulariopsis species. In most instances, particularly if a patient does not have underlying immunologic or hematologic disease, Scopulariopsis species should be considered a contaminant when recovered from a sputum specimen. However, if there is clinical or X-ray evidence of mycotic pulmonary infection, additional daily induced sputum specimens should be obtained.
If Scopulariopsis species or any other hyaline mold is recovered from two or more successive specimens, its potential as a pathogenic agent should be considered. Scopulariopsis species have been reported as the agents of pulmonary fungus ball infections in patients with preexistent cavities and as a cause of pneumonia in patients with leukemia.
Invasive pulmonary disease by this agent has not been reported.
The fungus illustrated in this photomicrograph was recovered from an induced sputum specimen from a 74 year old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This isolate is most likely:
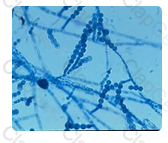
Hemoglobin F has a high affinity for oxygen. When Hb F is elevated, cells containing Hb S are more oxygenated and do not sickle as readily as they would if Hb F were not present or present in small quantities.
Which hemoglobin, when elevated, acts as a protection against sickling in patients with HbS?
The FTA-ABS is used to confirm that a positive non-treponemal test like RPR is not the result of a biological false positive, which occur in about 1 to 10 percent of the population.
A positive RPR test and a negative FTA-ABS test is most likely the result of:
Which of the following Rh antigens is found the highest frequency in the Caucasian population:
The results of this PT and aPTT are in normal range. These results can be reported and are not indicative of the need to: order a mixing study or request a redraw.
You have just performed stat PT and aPTT tests on your coagulation instrument. Your results are as follows:
PT = 12 seconds (normal range 10-13 seconds)
aPTT = 24 seconds (normal range 21-34 seconds)
What would be your next step?
The conidia of Exophiala species are produced within phialides that extrude the conidia in tight, ball-like clusters.
The large, drum stick-shaped muriform macroconidia of Alternaria species are arranged in short chains; the small, elliptical conidia of Cladosporium species are arranged in both long and short, branching chains.
Which of the following dematiaceous fungal species produce conidia in clusters?
A young man is experiencing difficult breathing after fainting. The physician orders a blood gas analysis which shows the following results:
pH = 7.25
pCO2 = 62 mmHg
pO2 = 70 mmHg
HCO3 = 23 mEq/L
Which condition is most likely afflicting this patient?
To obtain a serum sample for a stat test on a patient receiving anticoagulant therapy, the recommended tube is:
Question options:
Donor and recipient blood samples (samples utilized for pre-transfusion compatibility testing) must be kept for at least 7 days after transfusion. Blood samples must be available to investigate a transfusion reaction, if necessary.
Donor and recipient blood samples must be kept for at least how long after transfusion?
The governmental agency that oversees public health care matters in the United States is:
The Westgard multi-rule 22S describes the scenario where two consecutive data points fall outside +2SD or -2SD. If this occurs, then the run must be rejected. This situation is most likely caused by a systematic error.
Which of the following describes the Westgard multi-rule 22S?
Post-hepatic obstruction is characterized by a marked increase in alkaline phosphatase, GGT, conjugated bilirubin, as well as other hepatic enzymes. The slight rise of ALT suggests that the issue is not hepatitis. Renal and cardiovascular failure do not match the symptom of jaundice or the abnormal laboratory values.
Chem
Which of the following conditions would be suggested by a jaundiced patient experiencing a marked rise in alkaline phosphatase, conjugated bilirubin, and a slight rise in ALT:
According to the Michaelis-Menton kinetics theory, when a reaction is performed in zero-order kinetics:
In combined fiscal years 2005 through 2009, transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) caused the higest number of reported fatalities (48%), followed by hemolytic transfusion reactions (26%) due to non-ABO (16%) and ABO (10%) incompatibilities. Complications of microbial infection, transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), and anaphylactic reactions each accounted for a smaller number of reported fatalities.
First, determine the number of WBC's from the hemocytometer as follows:
WBC count = (dilution ratio x # of cells counted x 10) / (# mm2 area counted)
Then: WBC count = (20 x 100 x 10) / (8) = 2500 WBC/mm3 (or 2500 WBC/uL or 2.5 x 103 WBC/uL)
Next, to find the WBC count per liter, multiply the WBC count/uL by the number of uL/L (there are 106 uL/L)
So: (2.5 x 103 WBC/uL) x (106 uL/L) = 2.5 x 109 WBC/L
Hematology
A 1:20 dilution is made for a manual WBC count. The four corner squares on both sides of a hemocytometer are counted. A TOTAL of 100 cells are counted in that area. What is the white blood cell count in terms of a liter (? x 10^9/L)?
Antidiuretic hormone, or ADH, has the important role of conserving body water by reducing the loss of water in urine by changing the water permeability of the distal tubule and collecting duct. An increase in ADH causes a concentrated urine since the water is retained and absorbed through the permeable membrane. An decrease in ADH causes the collecting ducts to retain very little water, instead it is excreted as urine.
Chemistry
Which of the following action describes the MAJOR property of antidiuretic hormone?
Alkaline over acid, or K/A, in TSI reactions is associated with the fermatation of glucose alone and the utilization of peptone.
Which of the following sugars has been fermented by a gram-negative rod that has produced an alkaline slant and an acid butt on triple sugar iron agar (TSI).?
Urinalysis & Other Body Fluids
Match the following urine chemical reagent strip test pads to the disease or disorder that would most likely cause a positive test result.
1. Ketones
2. Blood
3. Bilirubin
4. Nitrites
Dce is found in 4% of whites and 44% of blacks.
DCe is found in 42% of whites and 17% of blacks.
DcE is found in 14% of whites and 11% of blacks.
dce is found in 37% of whites and 26% of blacks.
Blood bank
The most common Rh haplotype among whites is:
Match each of the descriptions with the appropriate magnification:
1. Color, Rouleau, Overall Slide Quality, Cell Distribution
2. Platelet estimates RBC-platelet-WBC morphology WBC differential RBC inclusions
3. Select area to examine, WBC estimate
Plasma concentrations of creatinine are used to assess renal function. Creatinine clearance is based on the serum creatinine level and is used to measure glomerular filtration rate, or GFR.
An increased serum level of which of the following analytes is MOST commonly associated with decreased glomerular filtration?
A monoclonal B-cell population (Kappa or Lambda predominant) with expression of CD19, CD20, CD23, and co-expression of CD5 is consistent with which of the following?


