Refer to the exhibit which shows the Download Import Report.
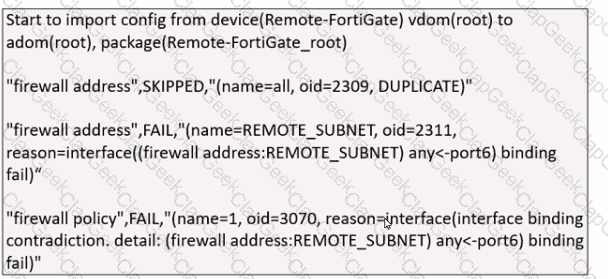
Why is FortiManager failing to import firewall policy ID 1?
You are moving managed FortiGate devices from one ADOM to a new ADOM.
Which statement correctly describes the expected result?
An administrator has assigned a global policy package to custom ADOM1. Then the administrator creates a new policy package. Fortinet. in the custom ADOM1. What happens to the Fortinet policy package when it is created?
Refer to the exhibit.
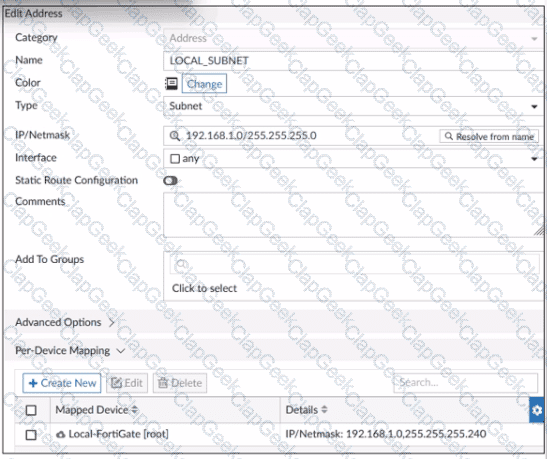
An administrator has created a firewall address object that is used in multiple policy packages for multiple FortiGate devices in an ADOM.
After the installation operation is performed, which IP/netmask is shown on FortiManager for this firewall address object for devices without a Per-Device Mapping set?
Exhibit.

Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, what are two results from this configuration? {Choose two.)
An administrator enabled workspace mode and now wants to delete an address object that is currently referenced in a firewall policy. Which two results can the administrator expect? (Choose two.)
Push updates are failing on a FortiGate device that is located behind a NAT device. Which two settings should the administrator check? (Choose two.)
If both FortiManager and FortiGate are behind NAT devices, what are the two expected results? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.

Which statement about the environment shown in the exhibit is correct?
Refer to the exhibit.
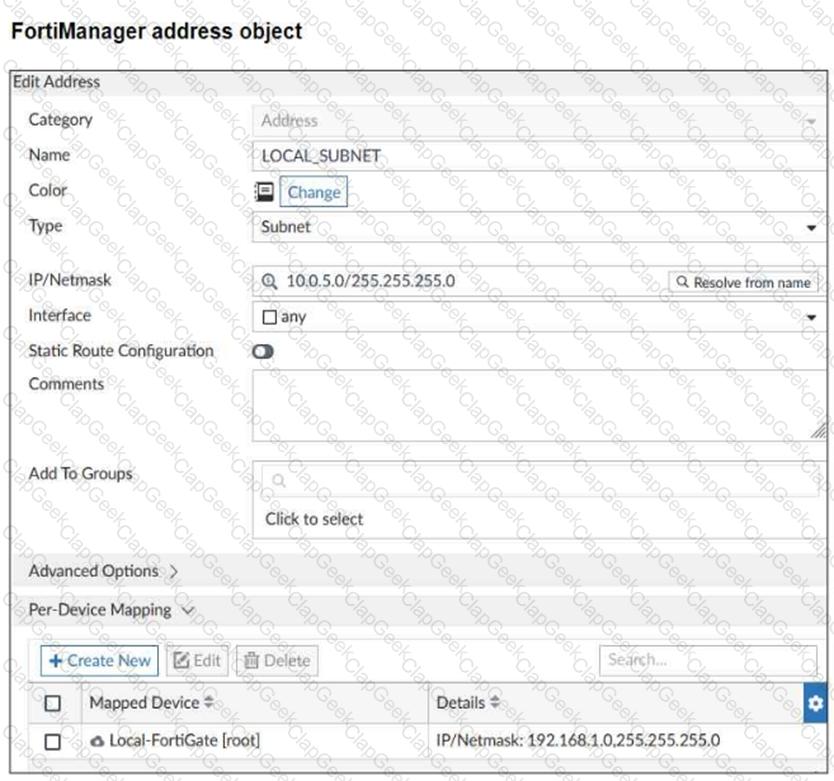
An administrator has created a firewall address object that is used in multiple policy packages for multiple FortiGate devices in an ADOM.
After the installation operation is performed, which IP/netmask will be installed on Local-FortiGate for theLOCAL_SUBNETfirewall address object?
An administrator is in the process of copying a system template profile between ADOMs by running the following command: execute fmprofile import-profile ADOM2 3547 /tmp/myfile Where does this command import the system template profile from?
Which two statements about scheduled backups on FortiManager are true? (Choose two.)
Which configuration setting for FortiGate is part of an ADOM-level database on FortiManager?
Refer to the exhibit.
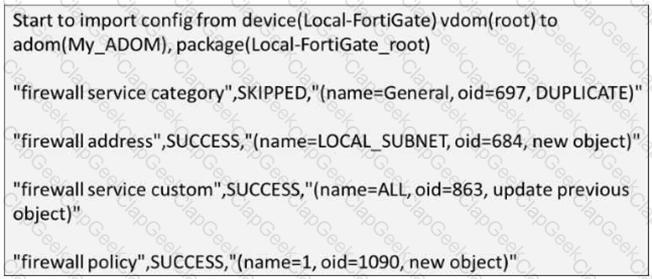
Given the import report shown in the exhibit, how did FortiManager handle the service category namedGeneral?


